🤖 Self-Service Automation Framework
📋 Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Logic and Workflow
- Creating Custom Automation
- Integration with Stacktic
- Getting Started
Introduction
Overview
Stacktic provides a logic automation framework that is completely open for customer use. This framework enables you to create custom automation and platform engineering solutions tailored to your specific needs.
📘 Note: This is a high-level explanation of the automation framework. For detailed implementation and syntax, please request the separate Self-Service Automation Guide.
Key Principles
| Principle | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Open Framework | Fully accessible to customers | Complete customization capability |
| Simple & Efficient | Associates code conditions to UI elements | Easy to understand and implement |
| Extensible | Build on top of existing automation | Leverage Stacktic's patterns |
| Flexible Integration | Mix custom and Stacktic automation | Best of both worlds |
Why Self-Service Automation?
We understand that customers might want to:
- ✅ Create their own automation patterns
- ✅ Customize stack platform engineering
- ✅ Fit automation exactly to their needs
- ✅ Maintain control over their automation logic
For these reasons, we've opened our framework for anyone to use and extend.
Logic and Workflow
Architecture Overview
The automation framework operates on a branch-based model where:
- Each component points to a specific automation branch
- Stacktic maintains shared automation patterns
- Customers create private automation integrated with Stacktic's automation
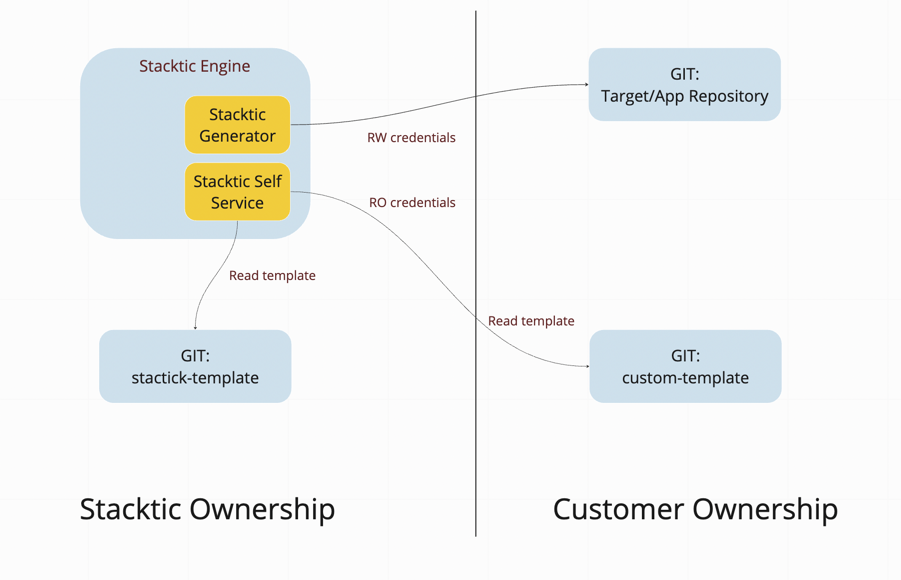
How It Works
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Component Definition | Each component references an automation branch |
| 2 | Shared Automation | Access Stacktic's maintained patterns |
| 3 | Custom Automation | Create your own private automation |
| 4 | Integration | Seamlessly blend custom and shared automation |
Automation Flow
Component Configuration
↓
Points to Automation Branch
↓
Combines:
- Stacktic Shared Automation (maintained)
- Customer Private Automation (custom)
↓
Generates Complete Stack Automation
Creating Custom Automation
Step 1: Add Component
Create new components with relationships and attributes:
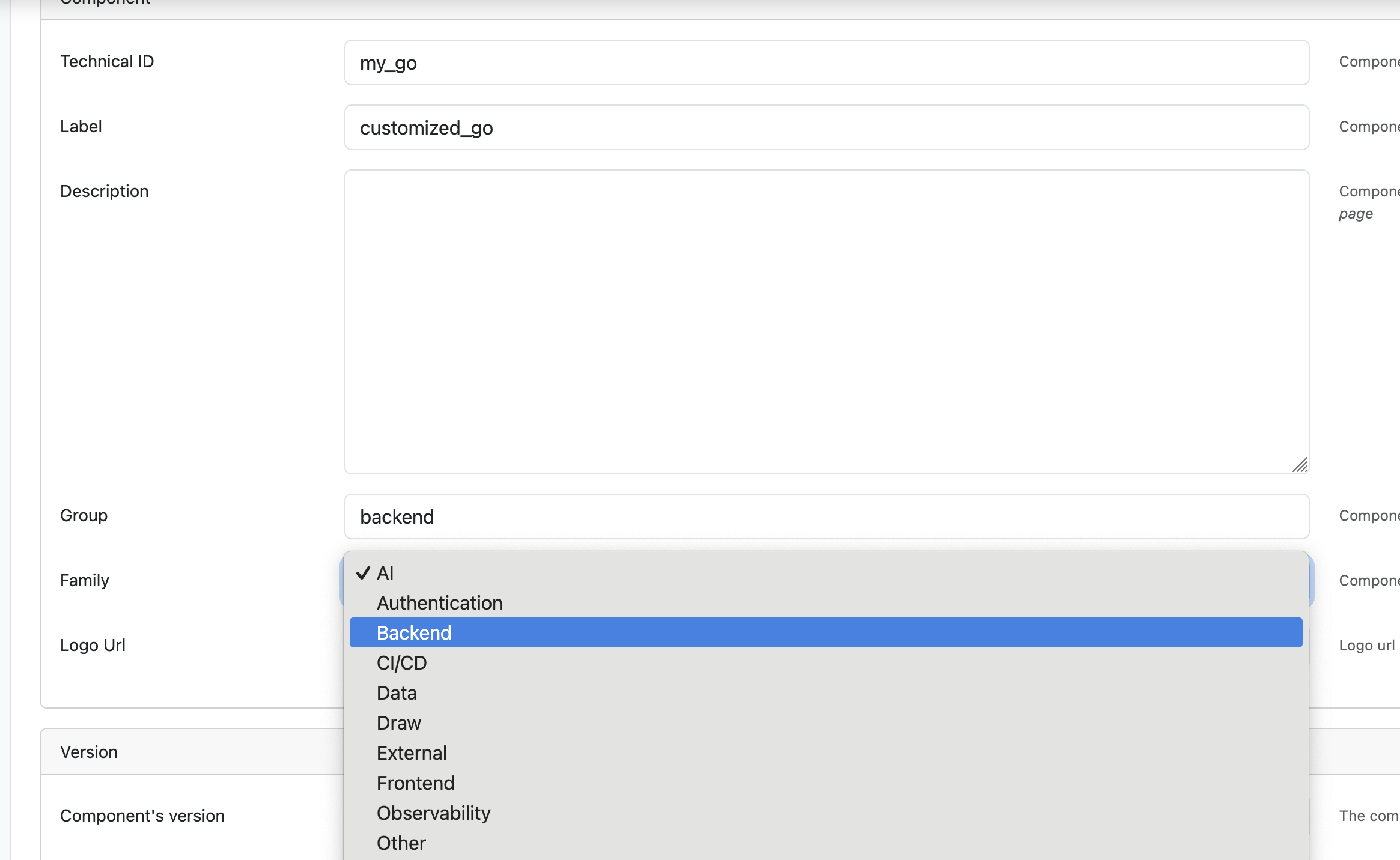
Component Definition includes:
- Component name
- Associated group
- Base configuration
- Automation branch reference
Step 2: Define Relationships
Add relationships to other components:
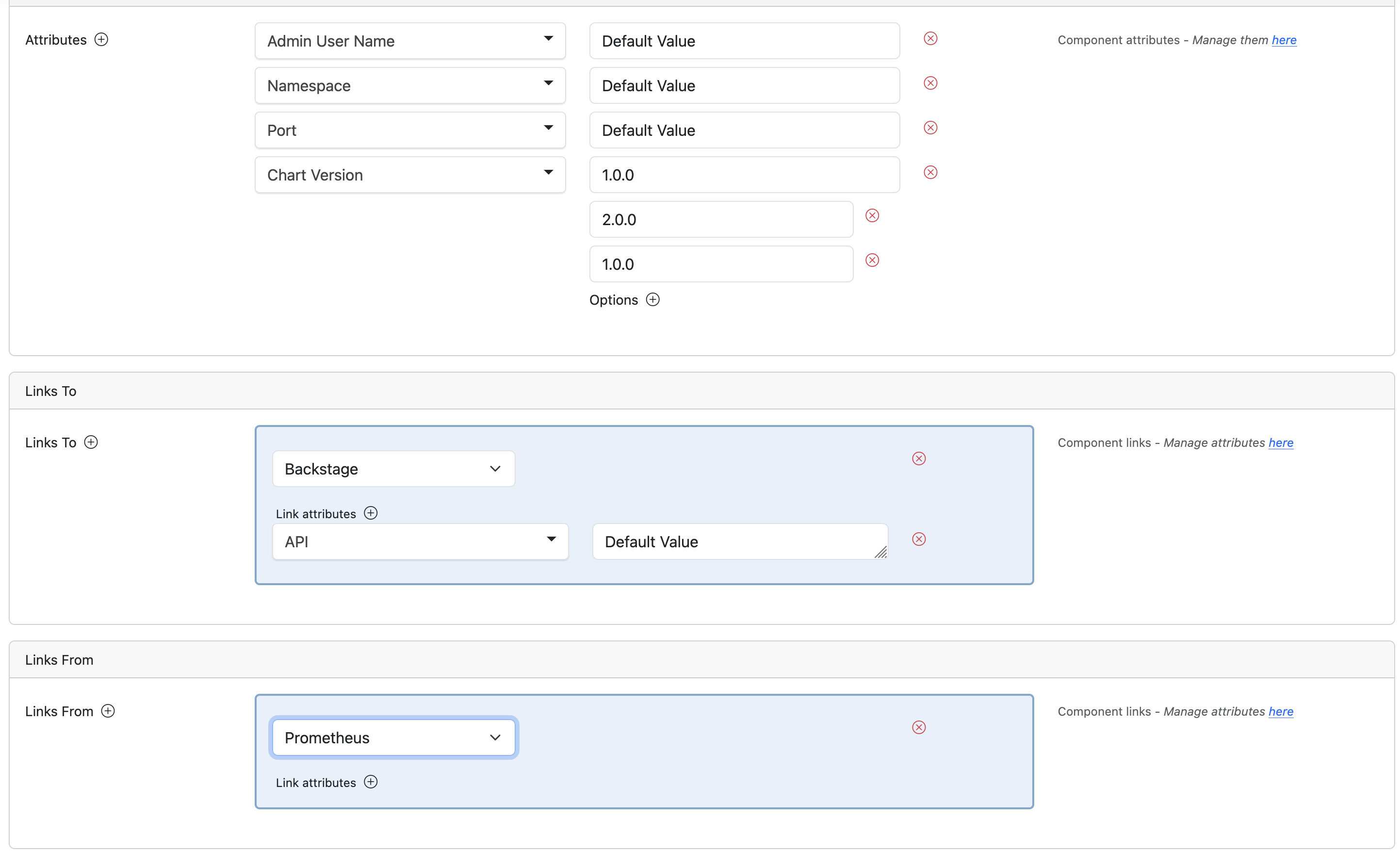
Relationship Configuration:
- Source component
- Target component
- Relationship type
- Data flow direction
- Automation triggers
Step 3: Point to Your Git
Connect to your automation repository:
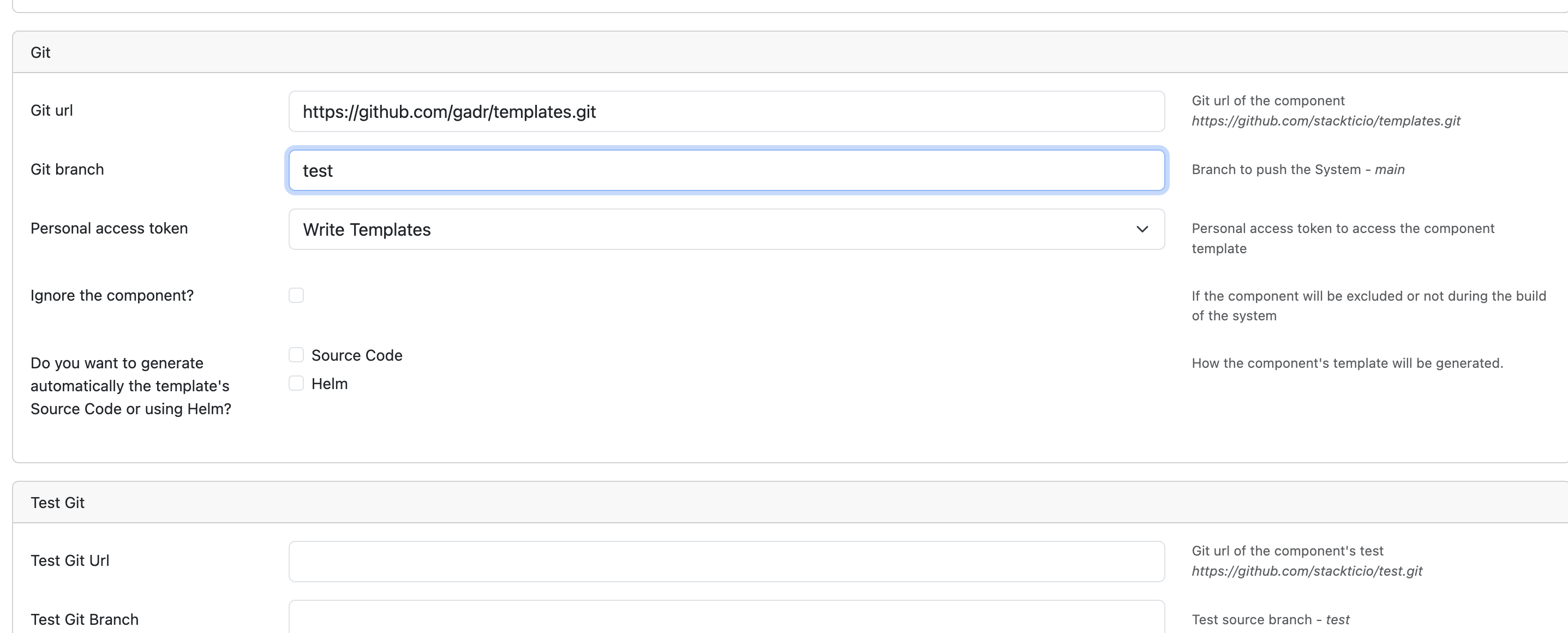
Git Integration:
- Reference your automation branch
- Maintain version control
- Enable collaborative development
- Track changes and updates
Integration with Stacktic
Hybrid Automation Model
| Automation Type | Maintained By | Purpose | Updates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Automation | Stacktic | Common patterns, best practices | Regularly updated |
| Private Automation | Customer | Custom logic, specific needs | Customer controlled |
| Combined Result | Automated | Complete stack automation | Real-time merge |
Benefits of Hybrid Approach
Leverage Stacktic's Expertise
- ✅ Use proven patterns
- ✅ Benefit from updates
- ✅ Avoid reinventing the wheel
Maintain Full Control
- ✅ Override when needed
- ✅ Add custom logic
- ✅ Protect proprietary patterns
Automation Capabilities
| Capability | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| UI Element Binding | Connect code to UI components | Dynamic interfaces |
| Conditional Logic | If/then automation rules | Complex workflows |
| Event Triggers | Respond to system events | Reactive automation |
| Data Transformation | Modify data between components | Integration patterns |
| Custom Validations | Add business rules | Compliance requirements |
Getting Started
Prerequisites
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Stacktic Account | Access to the platform |
| Git Repository | For your custom automation |
| Basic Understanding | Component and relationship concepts |
Next Steps
-
Request Documentation
- Contact us for the complete Self-Service Automation Guide
- Includes syntax, structure, and examples
-
Start Simple
- Begin with small customizations
- Build on Stacktic's shared automation
- Gradually add complexity
-
Best Practices
- Test automation in development first
- Version control all custom automation
- Document your patterns
- Share knowledge with your team
Support for Custom Automation
| Support Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Documentation | Complete syntax and structure guide available |
| Examples | Sample automation patterns provided |
| Consultation | Expert guidance for complex scenarios |
| Community | Share and learn from other users |
📧 Contact Us: For the complete automation syntax and structure guide, please contact our team. The framework is simple to use but requires the dedicated guide for implementation details.
🎯 Summary
Key Takeaways
The Stacktic Self-Service Automation Framework provides:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Open Access | Complete control over your automation |
| Simple Framework | Easy to learn and implement |
| Flexible Integration | Combine custom and shared patterns |
| Version Control | Git-based automation management |
| Extensible Platform | Grow and adapt as needed |
The Power of Self-Service
With Stacktic's automation framework, you're not limited to pre-built patterns. Create exactly what you need while leveraging our proven automation library.
This approach ensures:
- ✅ No vendor lock-in - Your automation is yours
- ✅ Rapid customization - Build what you need
- ✅ Best practices included - Start with proven patterns
- ✅ Future flexibility - Adapt as requirements change
Stacktic Automation Framework: Your logic, your way, powered by our platform.