📚 Automation Examples
📋 Table of Contents
- Overview
- RabbitMQ Automation
- Kafka/Strimzi Automation
- FastAPI Automation
- k6 Load Testing Automation
- Best Practices
- Additional Resources
Overview
This chapter provides real-world examples of service automation and relationships generated by Stacktic. These examples demonstrate how Stacktic automates configurations based on best-practice patterns, creating the necessary resources, documentation, and relationships to support full-stack demands.
Important Notes
⚠️ Scope Notice: These are examples only, not complete automation implementations.
The full automation is generated into your target repository's documentation with all configurations, secrets, and operational procedures.
What Gets Automated
| Service | Automated Components | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| RabbitMQ | Exchanges, queues, bindings, users | Message flow configuration |
| Kafka | Topics, bridges, connectors, sinks | Event streaming setup |
| FastAPI | Routes, endpoints, documentation | API gateway integration |
| k6 | Test scripts, CRDs, plugins | Performance testing |
🐇 RabbitMQ Automation
Component Architecture
RabbitMQ automation demonstrates how Stacktic handles message queue patterns with sub-components and relationships.
Sub-Component Creation
You can create sub-components such as:
- Exchanges - Message routing logic
- Queues - Message storage
- Bindings - Flow definitions between exchanges and queues
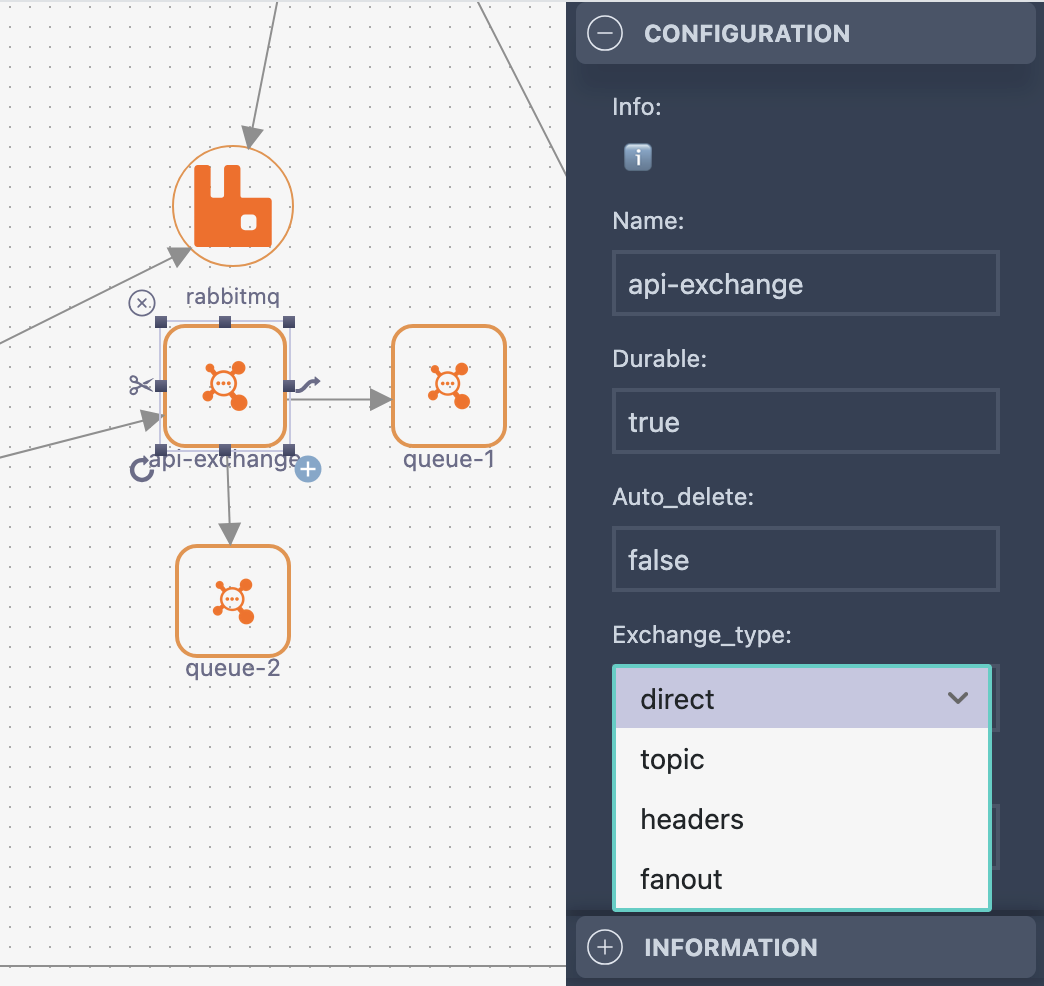
Relationship Configuration
The link between an exchange and a queue represents the binding configuration:
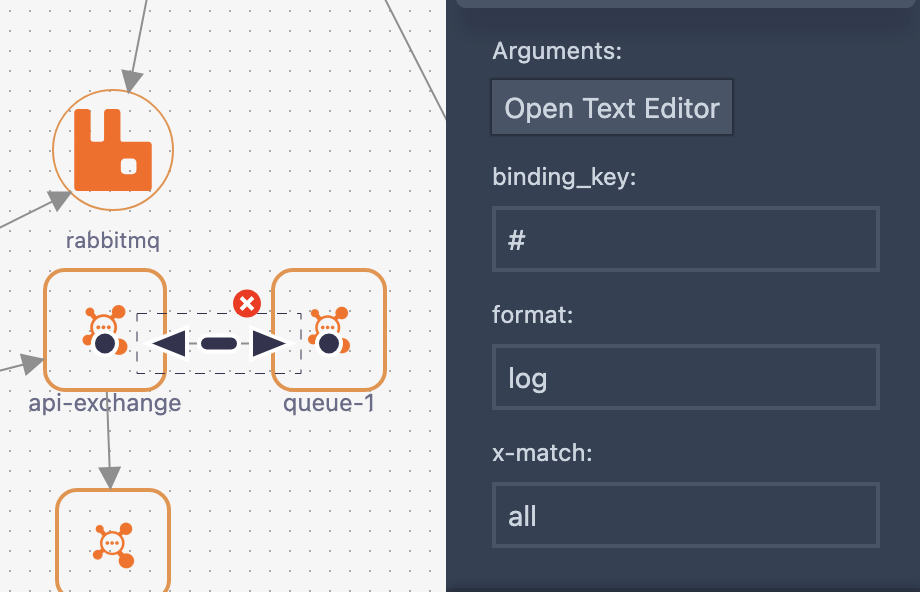
Generated Configuration
Secret Configuration Example
The automation generates a complete RabbitMQ configuration stored as a Kubernetes secret:
cat k8s/deploy/base/rabbitmq/secret/definitions.json
{
"vhosts": [
{ "name": "/" }
],
"users": [
{
"name": "user",
"password_hash": "EJBKv6SgKs6UFaLurzia3tPUIxQ/d4NIfwXG0OUWD2ayoCRd",
"tags": "management"
},
{
"name": "admin",
"password_hash": "C5pNaWoy+Fb7WeHsIgtP/6DvaimpRJkdo4BQQYlO+yluv0b/",
"tags": "administrator"
}
],
"permissions": [
{ "user": "user", "vhost": "/", "configure": ".*", "write": ".*", "read": ".*" },
{ "user": "admin", "vhost": "/", "configure": ".*", "write": ".*", "read": ".*" }
],
"parameters": [],
"global_parameters": [
{ "name": "cluster_name", "value": "rabbit@my-rabbit" }
],
"policies": [],
"bindings": [{
"source": "api-system",
"destination": "systems",
"destination_type": "queue",
"vhost": "/",
"routing_key": "#"
}],
"queues": [{
"name": "systems",
"vhost": "/",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {}
}],
"exchanges": [{
"name": "api-system",
"type": "topic",
"vhost": "/",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"internal": false,
"arguments": {}
}]
}
Additional Configurations
| Configuration Type | Location | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Versioning | Component level | RabbitMQ version management |
| Resources | Component attributes | CPU/Memory allocation |
| Security | Component & links | Authentication, TLS, network policies |
| Monitoring | Auto-generated | Prometheus metrics, Grafana dashboards |
📝 Note: Additional configuration related to versioning, resources, and security exists within the RabbitMQ component itself.
🦄 Kafka Automation
Advanced Event Streaming
Kafka Strimzi is a more complex component but follows similar automation principles.
Sub-Component Types
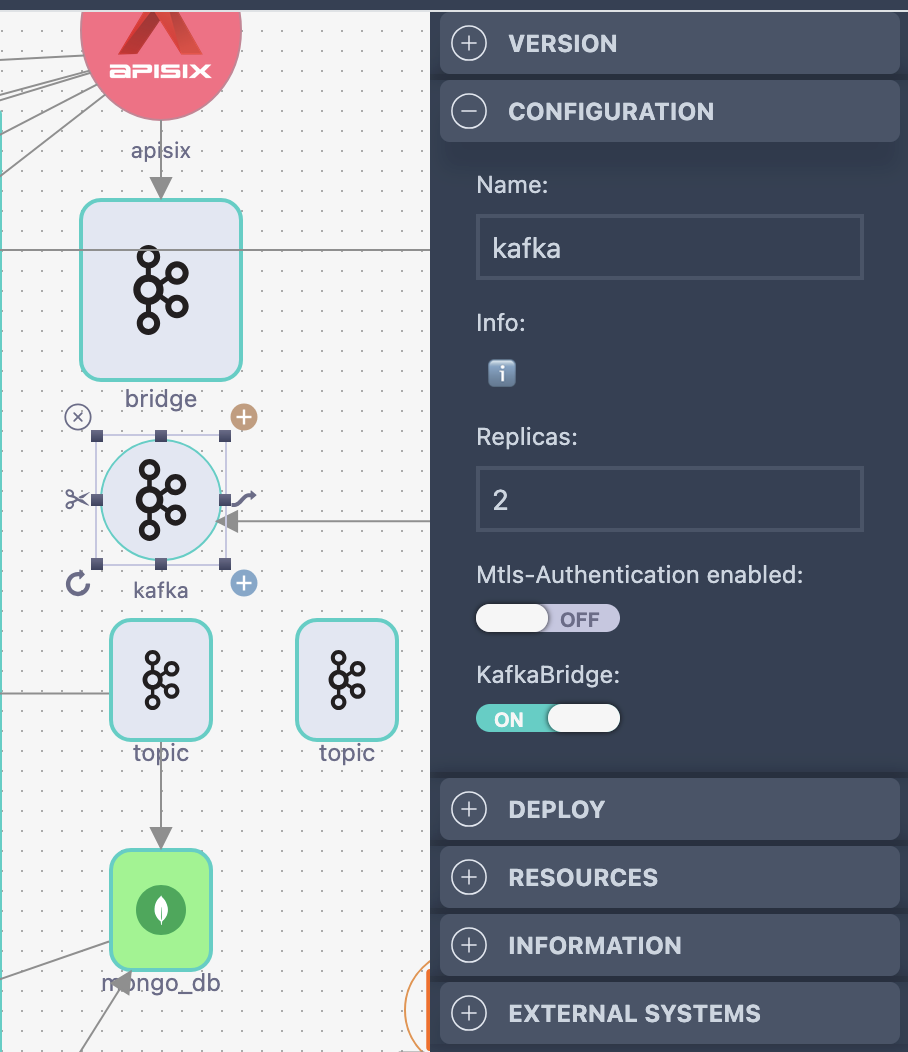
| Sub-Component | Purpose | Automation Features |
|---|---|---|
| Topics | Event streams | Partitions, replication, retention |
| Bridges | HTTP integration | REST API exposure |
| Connectors | External systems | Database sinks, source connectors |
| Users | Access control | ACLs, authentication |
Integration Capabilities
API Gateway Integration
- Bridge connects to API gateway
- Integrates with OIDC via Keycloak
- Automatic authentication setup
Database Integration
- Topic sub-components connect to databases for sink operations
- Automated Kafka Connect configuration
- End-to-end setup including connectors and secrets
Example Resources
Demo Repository
Explore a sample implementation (not full automation):
🔗 Basic Strimzi Setup
Connectors Example
Review automated connector configurations:
🔗 Kafka Connectors
Automated Components
| Component | Generated Assets |
|---|---|
| Kafka Cluster | StatefulSets, services, config |
| Kafka Connect | Deployment, connector definitions |
| Schema Registry | Deployment, schemas |
| Monitoring | JMX exporters, dashboards |
⚡ FastAPI Automation
API Development Acceleration
FastAPI automation streamlines API configuration and documentation through intelligent relationship management.
Automatic Configuration
When you connect FastAPI to a queue or database, Stacktic automatically:
| Action | Generated Assets |
|---|---|
| Adds dependencies | Python packages, requirements.txt |
| Configures routes | API endpoints, middleware |
| Creates services | Business logic templates |
| Generates endpoints | GET, POST, DELETE, PUT methods |
| Documents APIs | OpenAPI/Swagger specs |
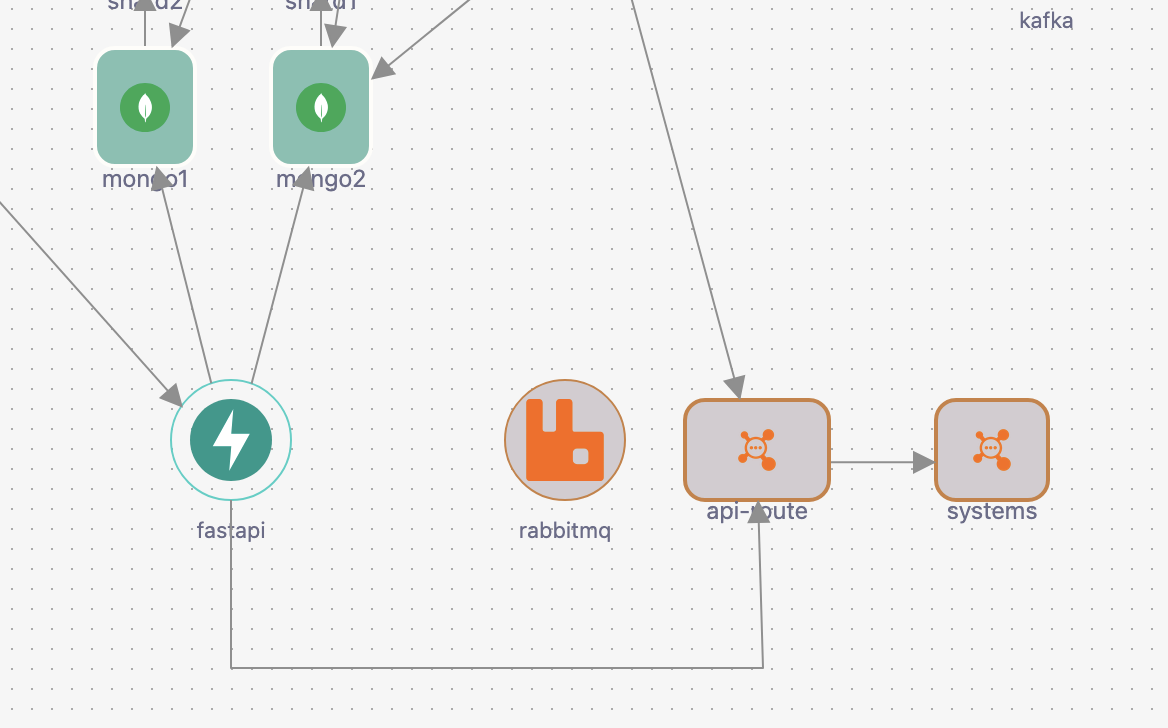
API Gateway Integration
Connect FastAPI to APISIX API Gateway for production-ready deployment:
- Automatic route registration
- Load balancing configuration
- Health check setup
- Rate limiting rules
Validation & Testing
Validate the configuration by testing the FastAPI endpoints and viewing generated documentation:
sub_component for custom API
Stacktic acts as version control for your stack.
You can:
- Create your own API on the existing FastAPI service in the
mainbranch. - Modify an existing API.
- Or use sub-components to define APIs.
When you add a sub-component, Stacktic automatically generates the API code inside the existing structure.
You don’t need to manually touch main—just add the route and basic service definition.
✅ Advantages of Using Sub-Component APIs
- Saved as part of Stacktic’s version control, making it easy to track changes.
- Minimizes direct code editing—no need to manage dependencies or modify
main; simply provide the API definition. - Gives Stacktic additional metadata about your logic, enabling smarter automation and insights.
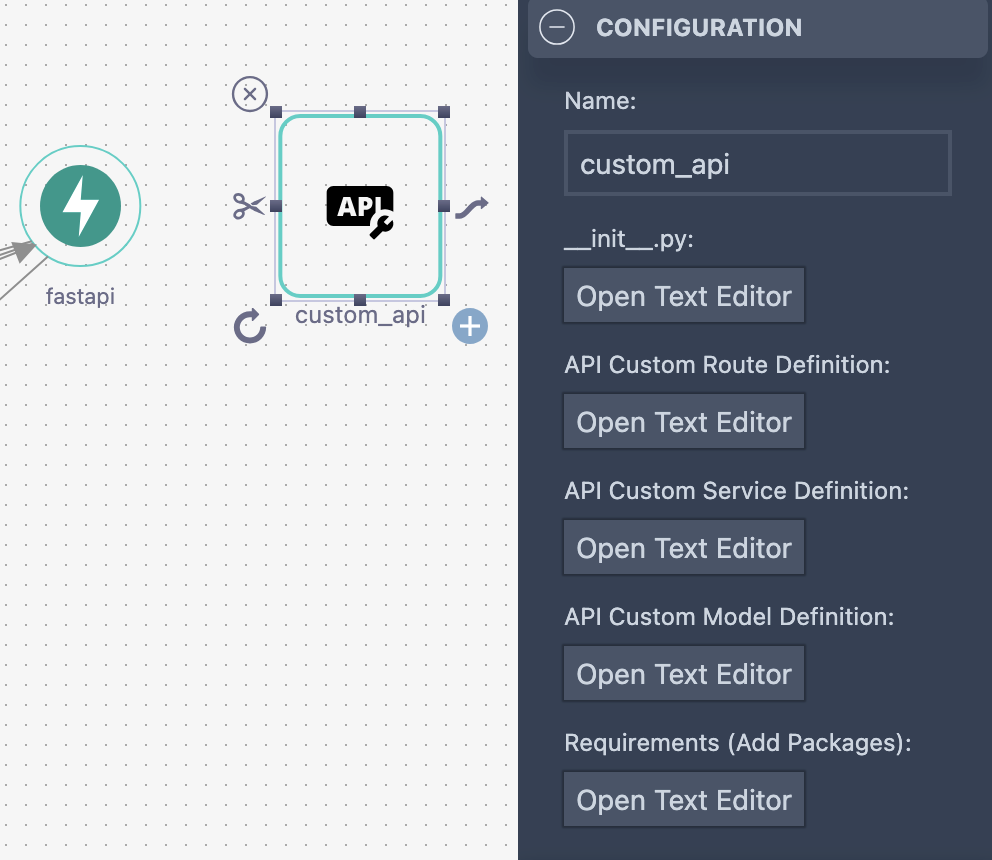
Security Best Practices
🔒 Security Recommendation:
We recommend external authentication instead of relying solely on FastAPI's built-in API key system.
OIDC Integration with APISIX & Keycloak
Use APISIX and Keycloak for enterprise-grade authentication:
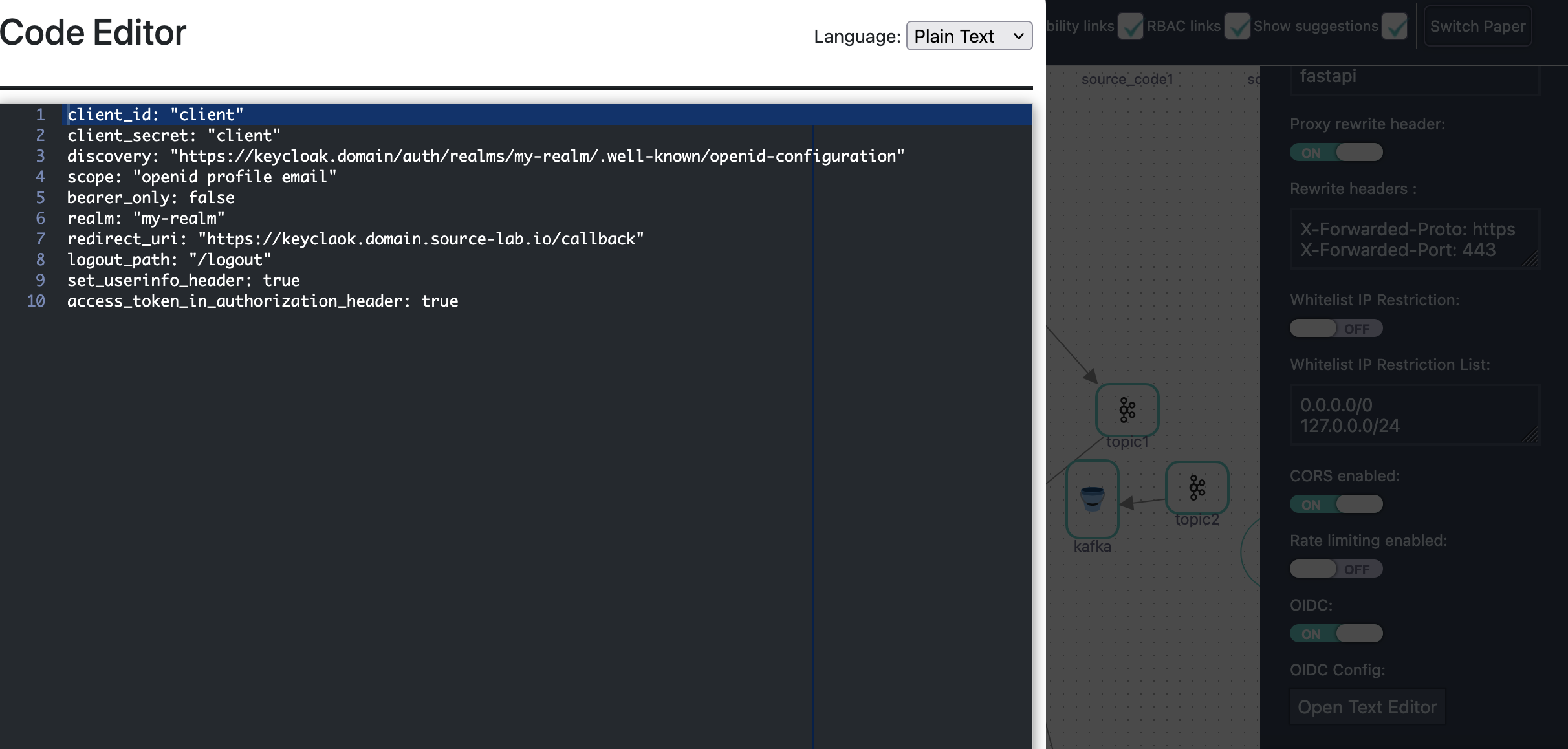
Benefits:
- ✅ Centralized authentication
- ✅ OIDC/OAuth2 support
- ✅ Single Sign-On (SSO)
- ✅ Token-based security
- ✅ Role-based access control
Configuration Details
| Configuration | Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Versioning | Component | Python version, FastAPI version |
| Admin Credentials | Component | Initial admin setup |
| Resources | Component | CPU/Memory limits |
| Build Image | Link | Required when linking APIs |
💡 Build Note: Build image is required when linking APIs to ensure dependency compatibility.
📈 k6 Load Testing Automation
Performance Testing Framework
To quickly assess your stack's performance and scaling configuration, link k6 to any service component.
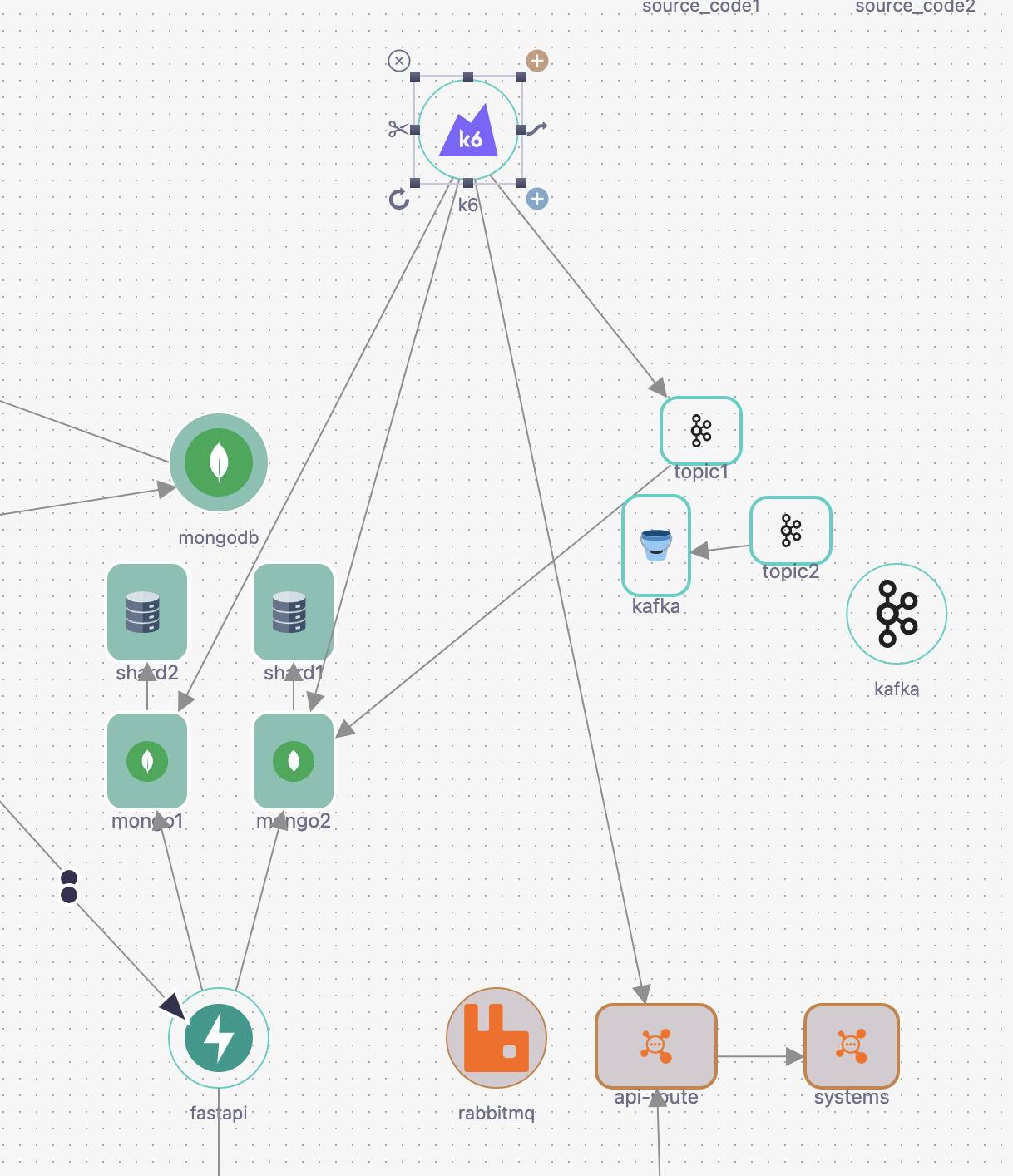
Automated Test Generation
When k6 is linked to services, Stacktic automatically:
| Action | Generated Output |
|---|---|
| Creates test files | k6 JavaScript test scripts |
| Builds CRDs | Kubernetes custom resources |
| Configures plugins | Database, queue, API plugins |
| Sets up reporting | Metrics collection, dashboards |
Example k6 Structure
tree k8s/deploy/base/k6
k8s/deploy/base/k6
├── k6.yaml # k6 operator configuration
├── kustomization.yaml # Kustomize manifest
├── mongodb_collector.yaml # MongoDB metrics collector
├── namespace.yaml # k6 namespace
├── secret
│ ├── cloud.env # Cloud configuration
│ └── registry.json # Registry credentials
├── test-run.yaml # Test execution definitions
└── tests
├── cnpg.js # PostgreSQL tests
├── kafka.js # Kafka tests
├── mongo.js # MongoDB tests
├── psql.js # PostgreSQL tests
└── rabbitmq.js # RabbitMQ tests
Test Execution Configuration
Sample test-run.yaml
apiVersion: k6.io/v1alpha1
kind: TestRun
metadata:
name: mongo-test
namespace: k6-operator-system
spec:
parallelism: 1
paused: "false"
quiet: "false"
script:
configMap:
name: k6-test-scripts
file: mongo.js
runner:
image: index.docker.io/asauer/k6:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
imagePullSecrets:
- name: registry-credential
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: k6-cm
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
---
apiVersion: k6.io/v1alpha1
kind: TestRun
metadata:
name: rabbitmq-test
namespace: k6-operator-system
spec:
parallelism: 1
paused: "false"
quiet: "false"
script:
configMap:
name: k6-test-scripts
file: rabbitmq.js
runner:
image: index.docker.io/asauer/k6:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
imagePullSecrets:
- name: registry-credential
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: k6-cm
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
Performance Testing Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated test creation | Tests generated from topology |
| One-time image build | Reusable across all tests |
| Integrated reporting | Results in Grafana dashboards |
| Scaling validation | Verify autoscaling configurations |
📊 Pro Tip: You only need to build the k6 image once—test definitions are referenced directly in the deployment through ConfigMaps.
📚 Best Practices
General Automation Guidelines
| Practice | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Start Simple | Begin with basic components | Easier troubleshooting |
| Use Sub-Components | Leverage hierarchical structure | Better organization |
| Define Relationships | Connect components properly | Automatic configuration |
| Test in Stages | Dev → Staging → Production | Risk mitigation |
| Review Generated Docs | Check automation outputs | Understanding & validation |
Security Recommendations
- External Authentication - Use OIDC providers over built-in auth
- Secret Management - Let Stacktic handle secret generation
- Network Policies - Enable auto-generated policies
- TLS Everywhere - Use encrypted connections
- Regular Updates - Keep component versions current
Performance Optimization
- ✅ Use k6 for baseline performance testing
- ✅ Configure resource limits appropriately
- ✅ Enable horizontal pod autoscaling
- ✅ Implement caching strategies
- ✅ Monitor with Prometheus/Grafana
🎯 Summary
Key Takeaways
✅ Pattern-Based Automation - Best practices built into every component
✅ Relationship Intelligence - Connections drive configuration
✅ Complete Stack Coverage - From messaging to testing
✅ Security by Default - Authentication, encryption, policies
✅ Production Ready - Generated configurations are deployment-ready
What's Automated vs. What You Control
| Stacktic Automates | You Control |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure configuration | Business logic |
| Service connections | Application code |
| Security policies | Data schemas |
| Monitoring setup | Business rules |
| Testing frameworks | Custom algorithms |
These examples demonstrate the power of Stacktic's automation. The full automation in your repository will include complete configurations, documentation, and operational procedures tailored to your specific stack.
Version: 2.0
Last Updated: September 2025
© Stacktic - Intelligent Stack Automation